Halobutyl rubber
Chlorobutyl and bromobutyl rubbers are an excellent choice for pharmaceutical stoppers and seals applications due to low levels of additives and impurities, high impermeability to moisture and air, chemical and biological inertness, resistance to aging and heat sterilization, and easiness to vulcanize using low levels of ‘clean’ curatives. However, outstanding physical and chemical properties come with a price. Halogenated butyl rubber is derived from combining butyl rubber with chlorine or bromine. During halogenation of elastomers, the low molecular weight oligomers C13H24 (CAS: 63251-38-7) and C21H40 (CAS: 2512216-71-4, which are always present in butyl rubbers, are converted partially into their halogenated versions, C13H23Cl (CAS: 63216-72-8), C13H23Br (CAS: 2514965-51-4), and C21H39Br (CAS: 2518227-14-8) (see typical chromatograms of chlorobutyl and bromobutyl rubber stopper headspace and extract). These chloro and bromo alkenes might affect the quality of pharmaceuticals when halobutyl rubber is used as a material for the container-closure system.
.
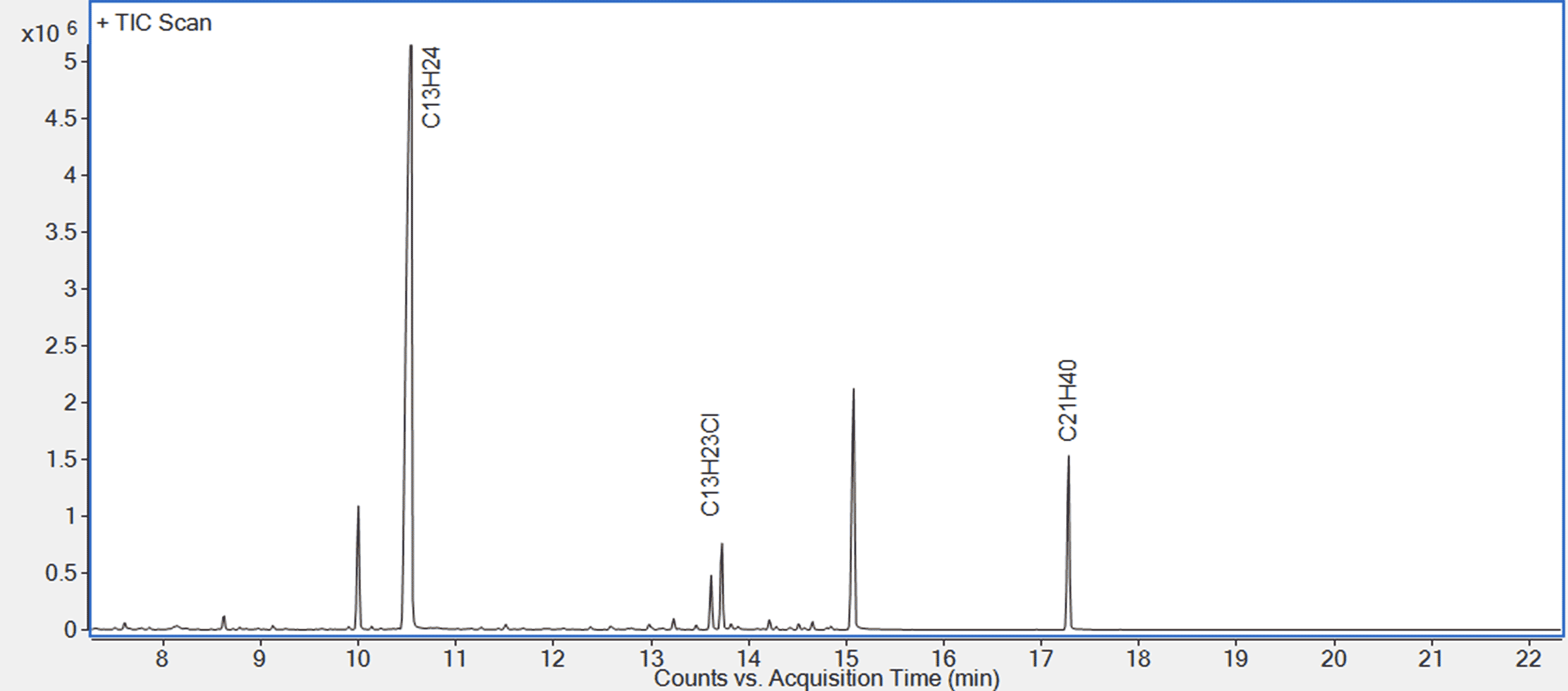
Figure 1. Typical head-space GC-MS chromatogram of chlorobutyl rubber stoppers. The labeled peaks indicate the presence of chlorinated and non-chlorinated elastomer oligomers
Figure 1. Typical head-space GC-MS chromatogram of chlorobutyl rubber stoppers. The labeled peaks indicate the presence of chlorinated and non-chlorinated elastomer oligomers
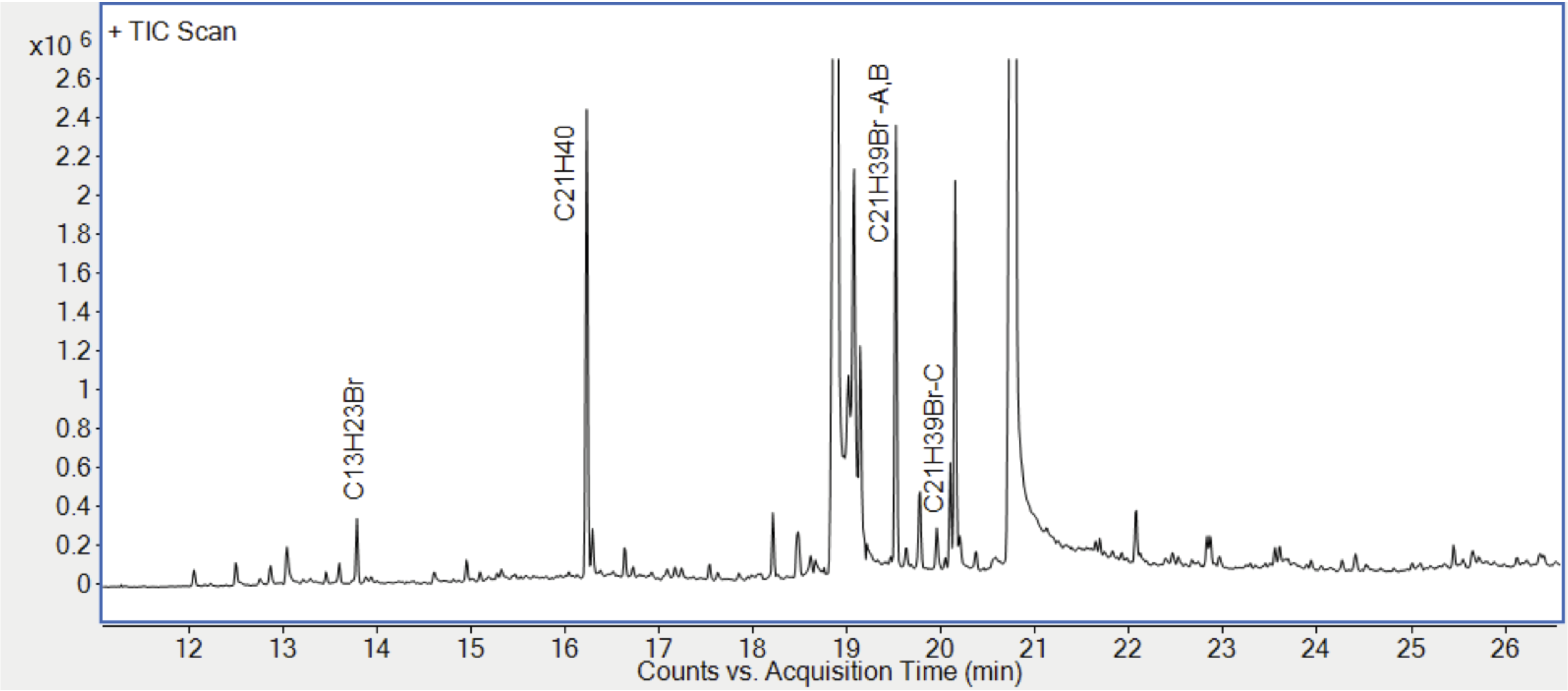
Figure 2. Typical GC-MS chromatogram of an isopropanol-water extract of bromobutyl rubber stopper. The labeled peaks indicate the presence of brominated and non-brominated elastomer oligomers
Figure 2. Typical GC-MS chromatogram of an isopropanol-water extract of bromobutyl rubber stopper. The labeled peaks indicate the presence of brominated and non-brominated elastomer oligomers
In the next section, you will learn why the migration of halogenated butyl rubber oligomers, C13H23Cl, C13H23Br, and C21H39Br, into drug products, should be monitored.
Why C13H23Cl, C13H23Br, and C21H39Br leachables must be under control
Why C13H23Cl, C13H23Br, and C21H39Br leachables must be
under control
It is necessary to establish that the packaging system used to store any pharmaceutical product is not leaching substances that may negatively affect its safety and efficacy.
There are two potential issues that the Cl-C13, Br-C13, and Br-C21 substances might cause when they migrate into the drug product: their carcinogenicity/mutagenicity and reactivity with drug products.
C13H23Cl, C13H23Br, and C21H39Br
are potentially mutagens
C13H23Cl, C13H23Br, and C21H39Br are
potentially mutagens
As it can be seen from the structures of the Br-C13 and Br-C21 compounds, they belong to the class of aliphatic halogens. The Toxtree software triggers a structural alarm for mutagenicity because aliphatic halogens are alkylating agents and might damage DNA.
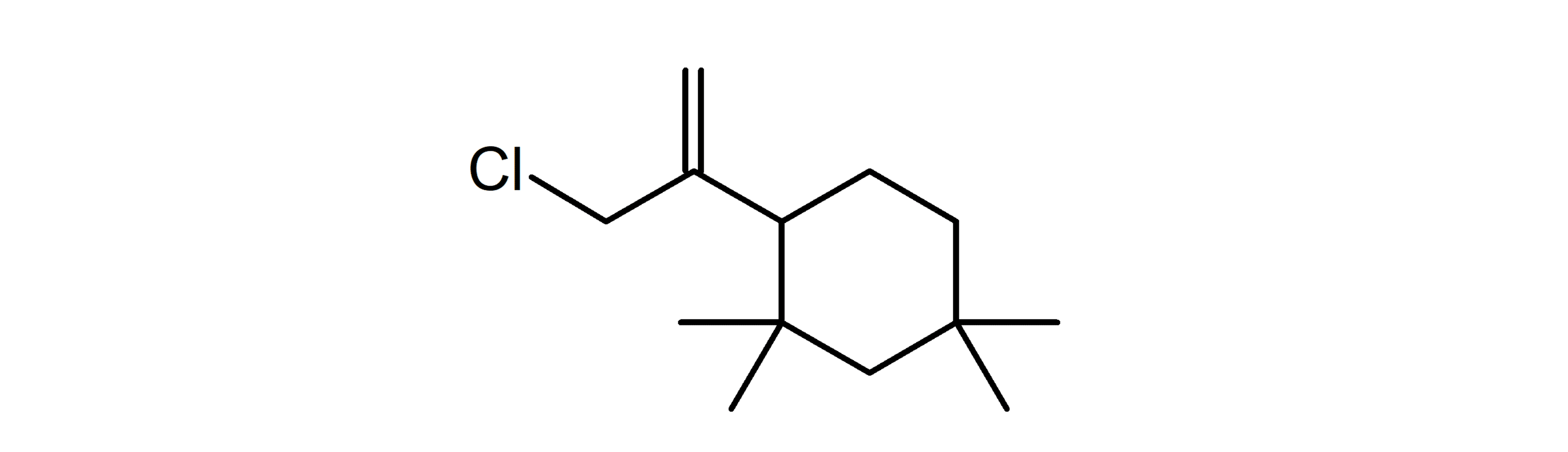
Figure 3. Structure of the Cl-C13 rubber oligomer
Figure 3. Structure of the Cl-C13 rubber oligomer

Figure 4. Structure of the Br-C13 rubber oligomer
Figure 4. Structure of the Br-C13 rubber oligomer
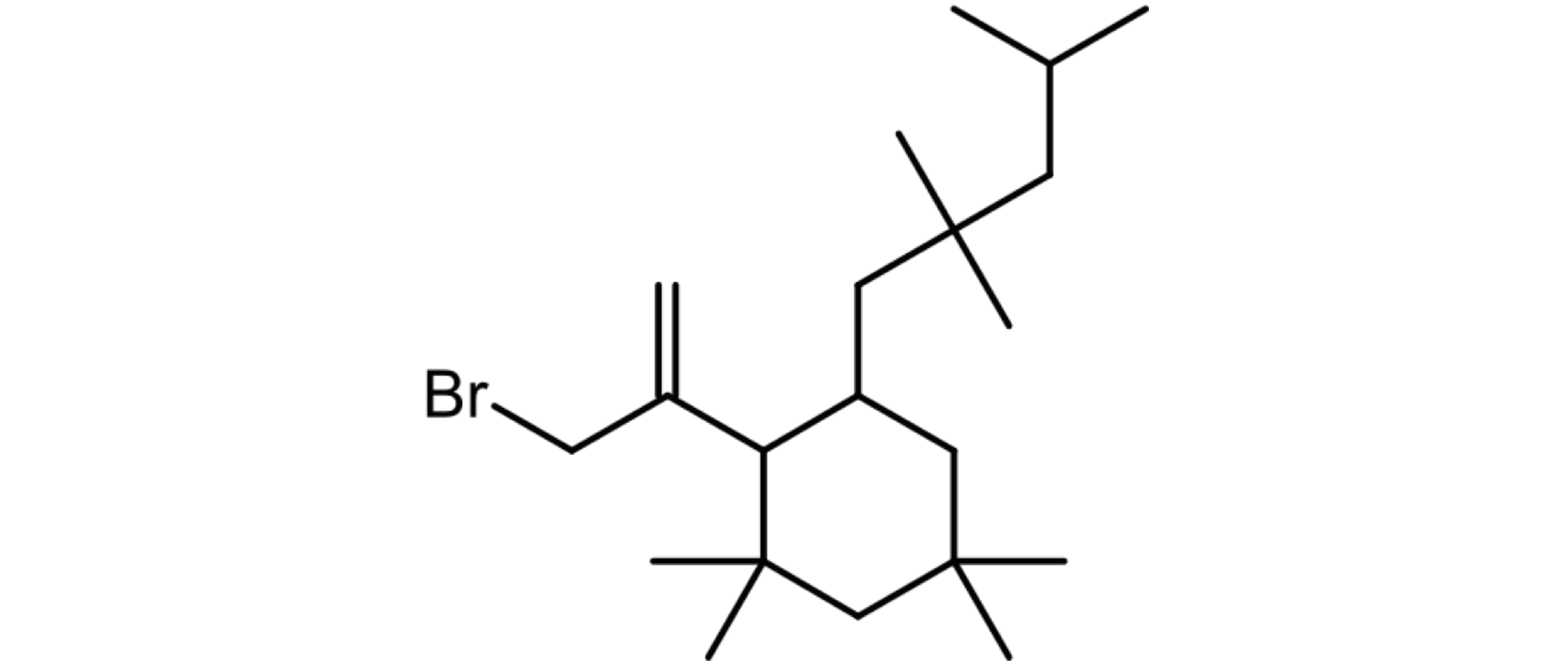
Figure 5. Structure of the main isomer of Br-C21 oligomer
Figure 5. Structure of the main isomer of Br-C21 oligomer
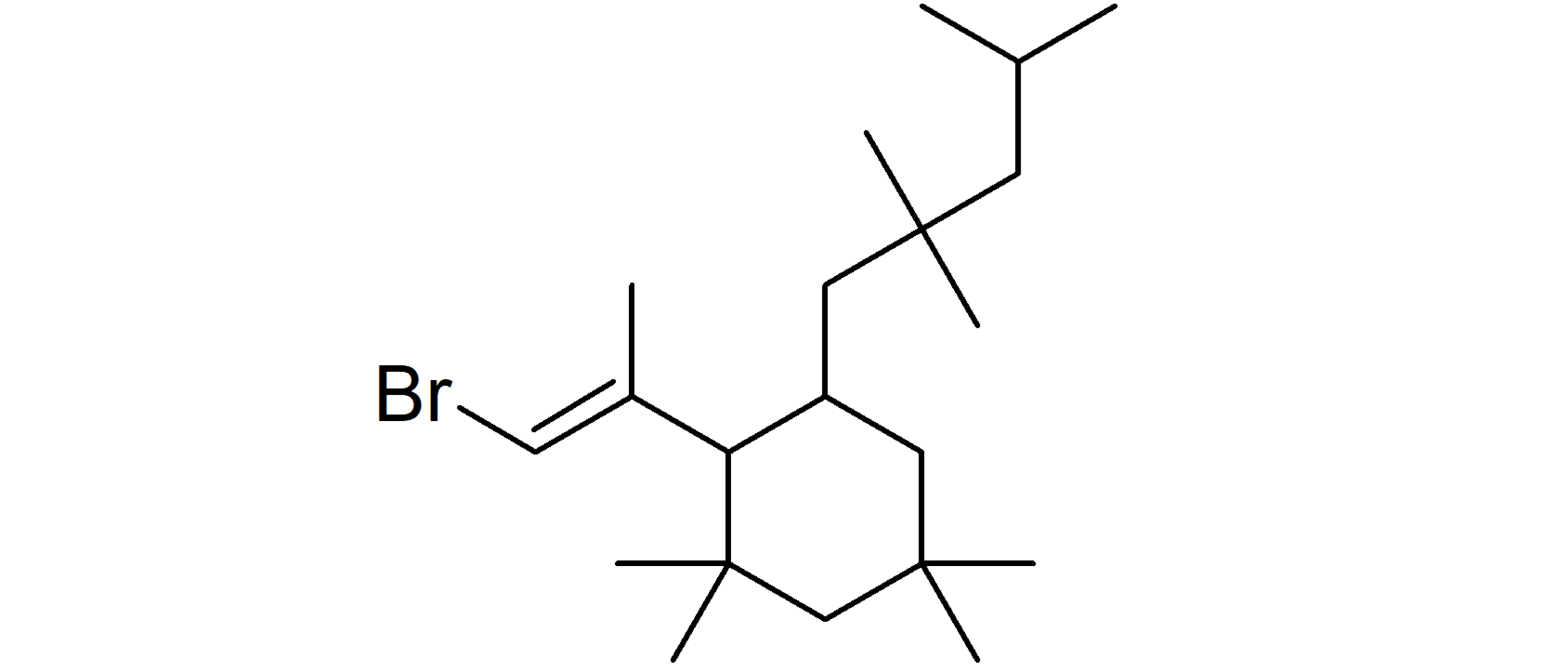
Figure 6. Structure of E-isomer of Br-C21 oligomer
Figure 6. Structure of E-isomer of Br-C21 oligomer
C13H23Cl, C13H23Br, and C21H39Br
are reactive leachables
C13H23Cl, C13H23Br, and C21H39Br are
reactive leachables
However, it is not only DNA that can react with the chlorinated and brominated rubber oligomers. If the API molecule contains nucleophilic centers, C13H23Cl, C13H23Br, and C21H39Br can alkylate them reducing the efficacy of the drug and generating impurities. For example, it has been shown that C13H23Br reacts with lyophilized insulin (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0B6nHWMZIXE at 23rd min).
How to monitor chlorinated rubber oligomer, C13H23Cl, and brominated rubber oligomers, C13H23Br and C21H39Br
The halogenated butyl rubber oligomers can be analyzed by GC-MS-based methods. Previously, the corresponding reference standards have not been available on the marked and surrogate standards have been employed for the determination of oligomeric rubber extractables and leachables. However surrogate substances do not provide an exact response match for the target analytes. Only authentical reference standards can guarantee the precision of the analysis.
Brominated rubber oligomers, C13H23Br and C21H39Br, are now available at Vit-n-Vivo
Brominated
rubber oligomers, C13H23Br and C21H39Br, are
now available
at Vit-n-Vivo
We at Vit-n-Vivo were able to isolate rubber oligomers and are offering now five reference materials: C13H23Cl rubber oligomer (RI 1418, CAS: 63216-72-8), C13H23Br rubber oligomer (RI 1501, CAS: 2514965-51-4), C21H39Br rubber oligomer (RI 2035, CAS: 2518227-14-8), the mixture of C21H39Br rubber oligomers (RI 1985 and 1990), as well as C21H40 (RI 1712, CAS: 2512216-71-4) rubber oligomer.
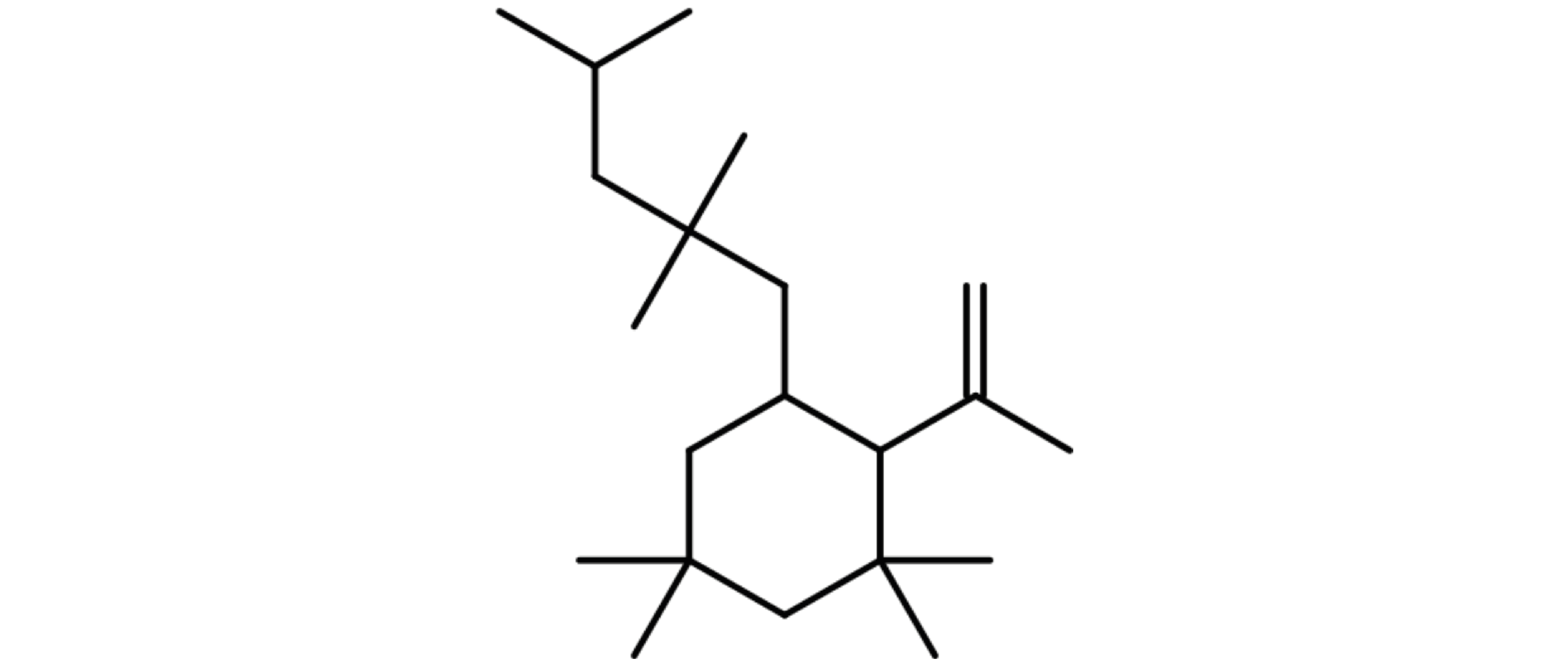
Figure 7. Structure of C21 non-halogenated rubber oligomer
Figure 7. Structure of C21 non-halogenated
rubber oligomer
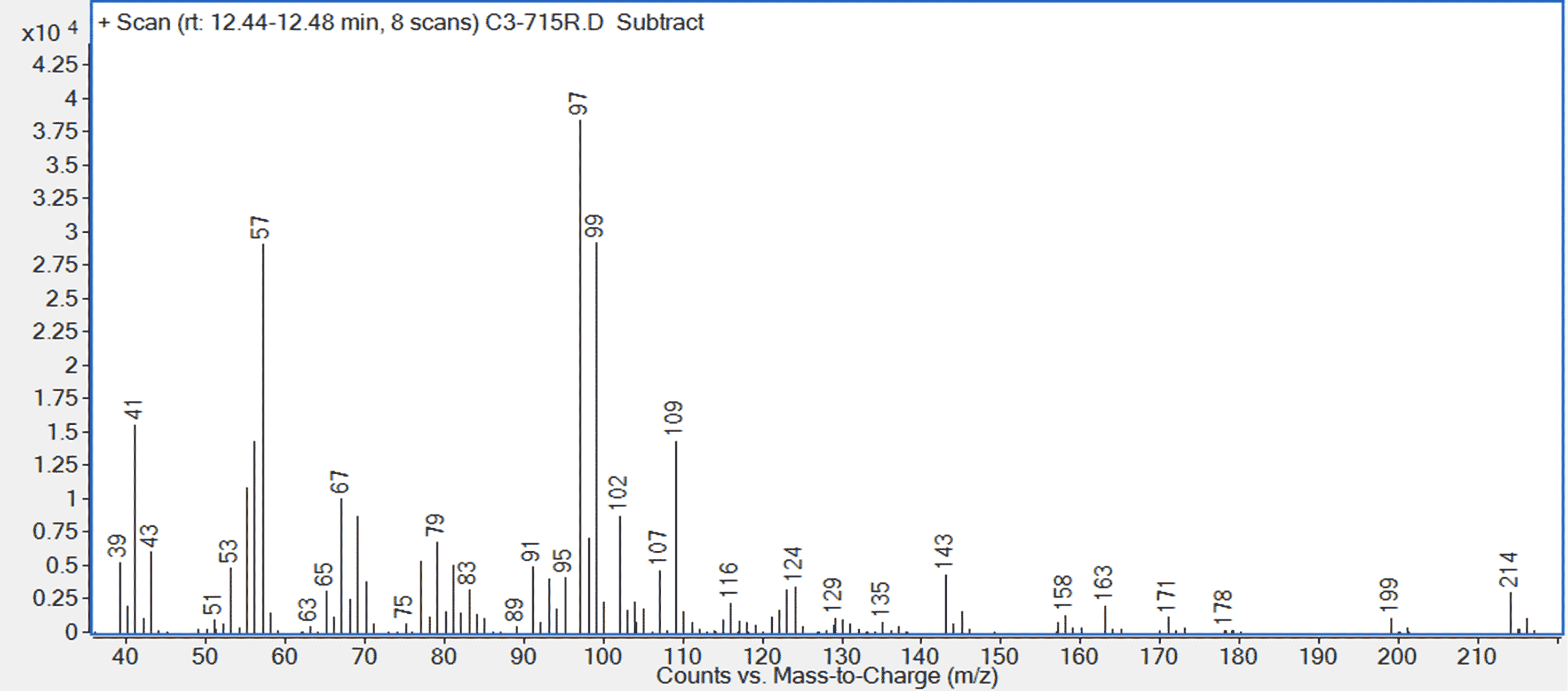
Figure 8. Mass spectrum of C13H23Cl rubber oligomer (RI 1418)
Figure 8. Mass spectrum of C13H23Cl rubber oligomer (RI 1418)
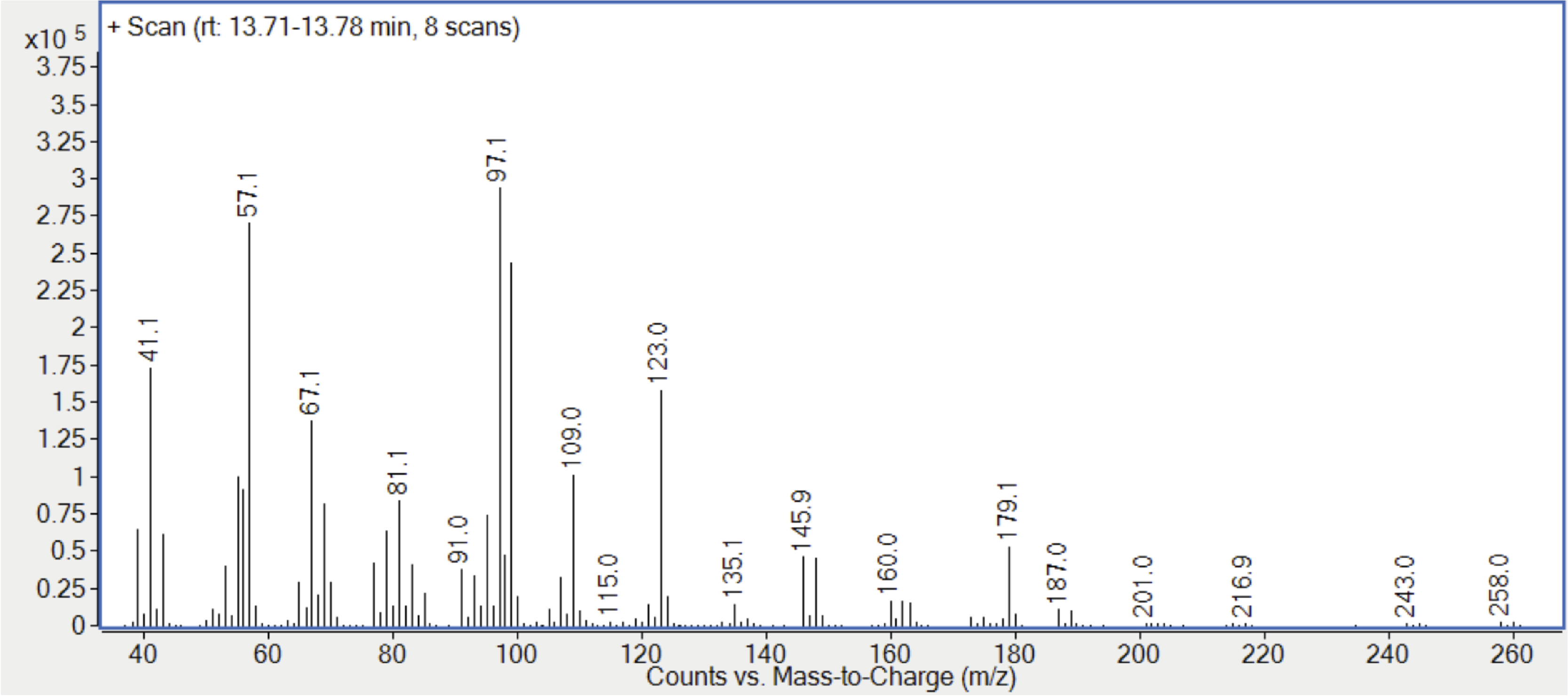
Figure 9. Mass spectrum of C13H23Br rubber oligomer (RI 1501)
Figure 9. Mass spectrum of C13H23Br rubber oligomer (RI 1501)
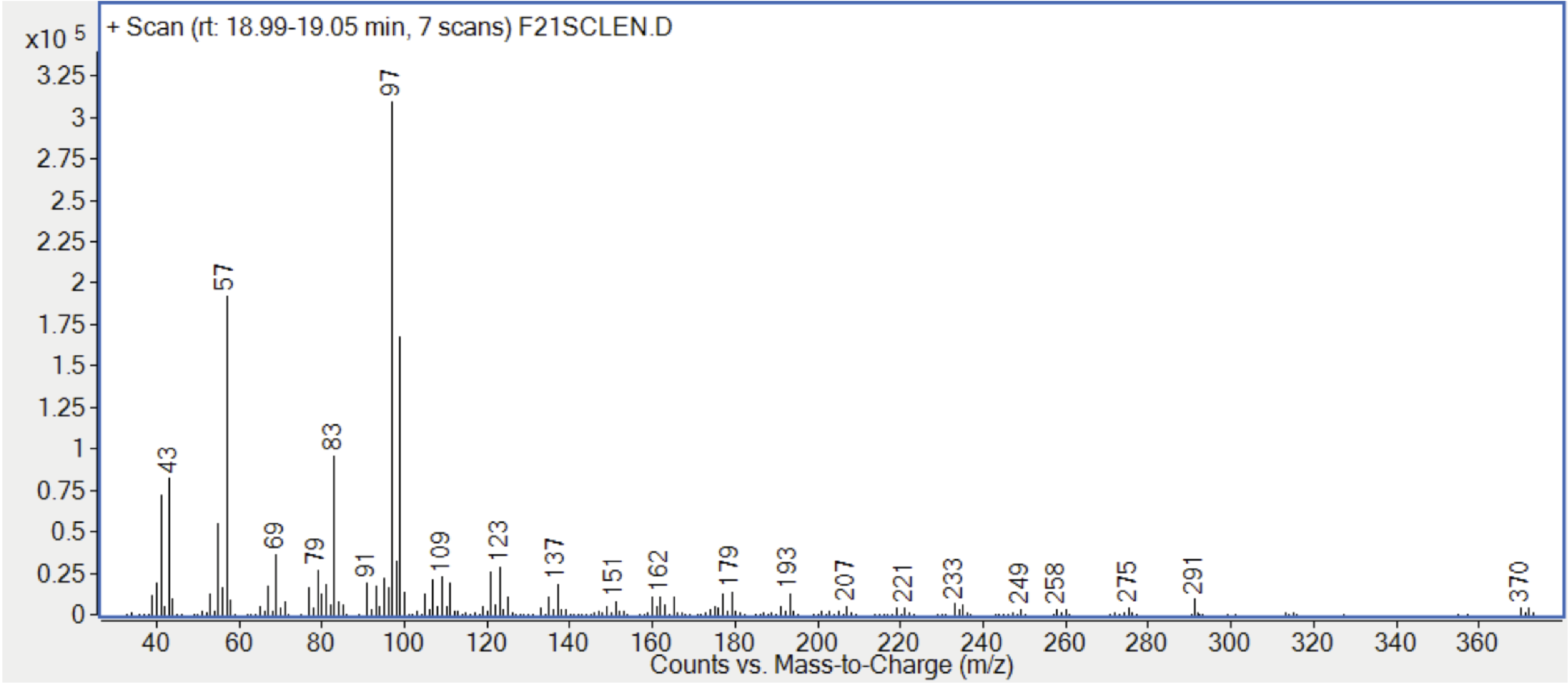
Figure 10. Mass spectrum of C21H39Br E-isomer (RI 1985)
Figure 10. Mass spectrum of C21H39Br E-isomer
(RI 1985)
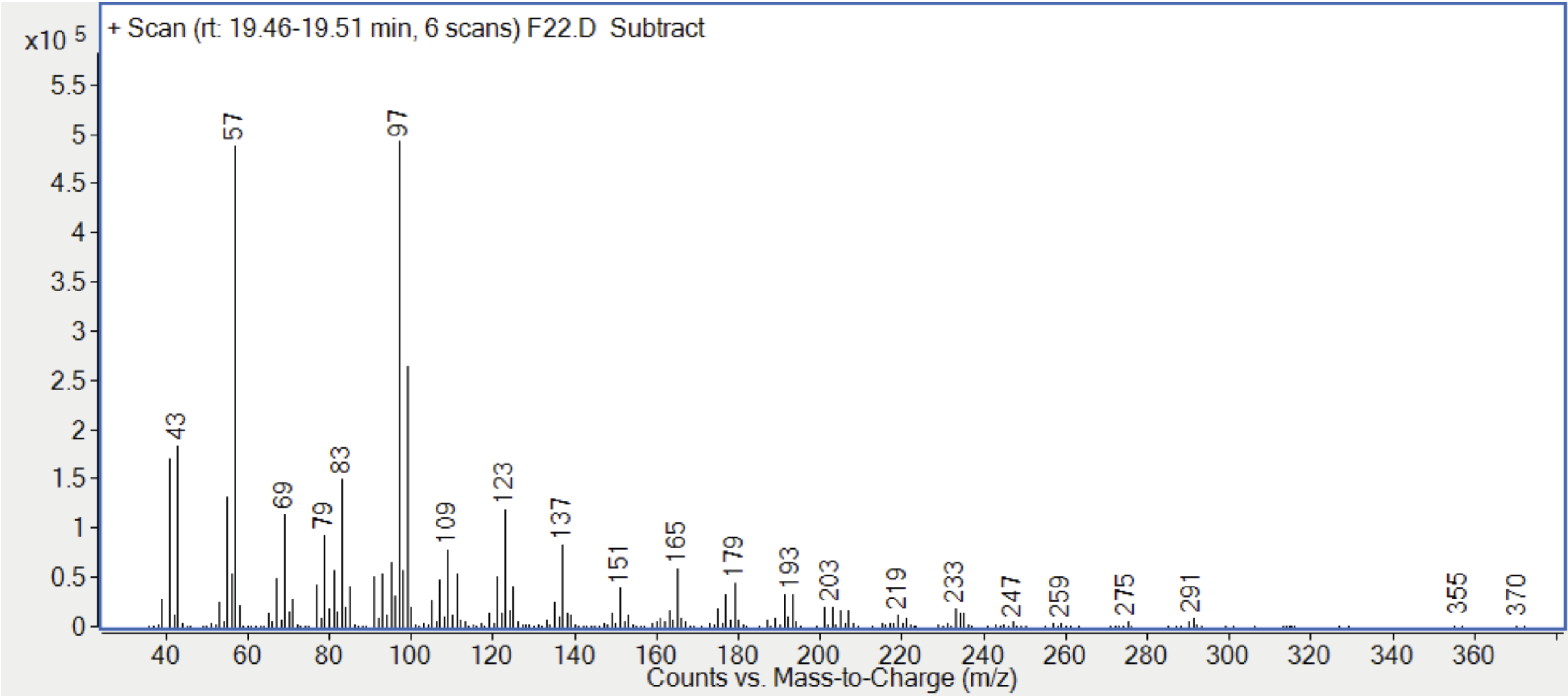
Figure 11. Mass spectrum of C21H39Br main isomer (RI 2035)
Figure 11. Mass spectrum of C21H39Br main
isomer (RI 2035)
Not sure if you have the halogenated rubber oligomers in your samples? Match the deconvoluted spectra with Vit-n-Vivo’s mass spectral library of rubber oligomers
Not sure if you have the halogenated rubber oligomers in your samples? Match the deconvoluted spectra with Vit-n-Vivo’s mass spectral library of rubber oligomers
First, download the compressed-n-Vivo’s mass spectral library of rubber oligomers and extract it into the NIST14MSSEARCH folder. The library is in NIST format and contains mass spectra of seven rubber oligomers:
- 1,1,5,5-tetramethyl-2-(prop-1-en-2-yl)cyclohexane; C13H24 (CAS: 63251-38-7)
- 1,1,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(1-methylethenyl)-3-(2,2,4-trimethylpentyl)cyclohexane; C21H40 (CAS: 2512216-71-4)
- 2-(1-(chloromethyl)ethenyl)-1,1,5,5-tetramethylcyclohexane; C13H23Cl (CAS: 63216-72-8)
- 2-(1-(bromomethy)lethenyl)-1,1,5,5-tetramethylcyclohexane; C13H23Br (CAS: 2514965-51-4)
- 2-[1-(bromomethyl)ethenyl]-1,1,5,5-tetramethyl-3-(2,2,4-trimethylpentyl)cyclohexane; C21H39Br-main isomer (CAS: 2518227-14-8)
- 2-[(1E)-1-bromoprop-1-en-2-yl]]-1,1,5,5-tetramethyl-3-(2,2,4-trimethylpentyl)cyclohexane; C21H39Br-E isomer
- 2-[(1Z)-1-bromoprop-1-en-2-yl]]-1,1,5,5-tetramethyl-3-(2,2,4-trimethylpentyl)cyclohexane; C21H39Br-Z isomer.
Second, include Vit-n-Vivo’s library in the Library spectrum Search.
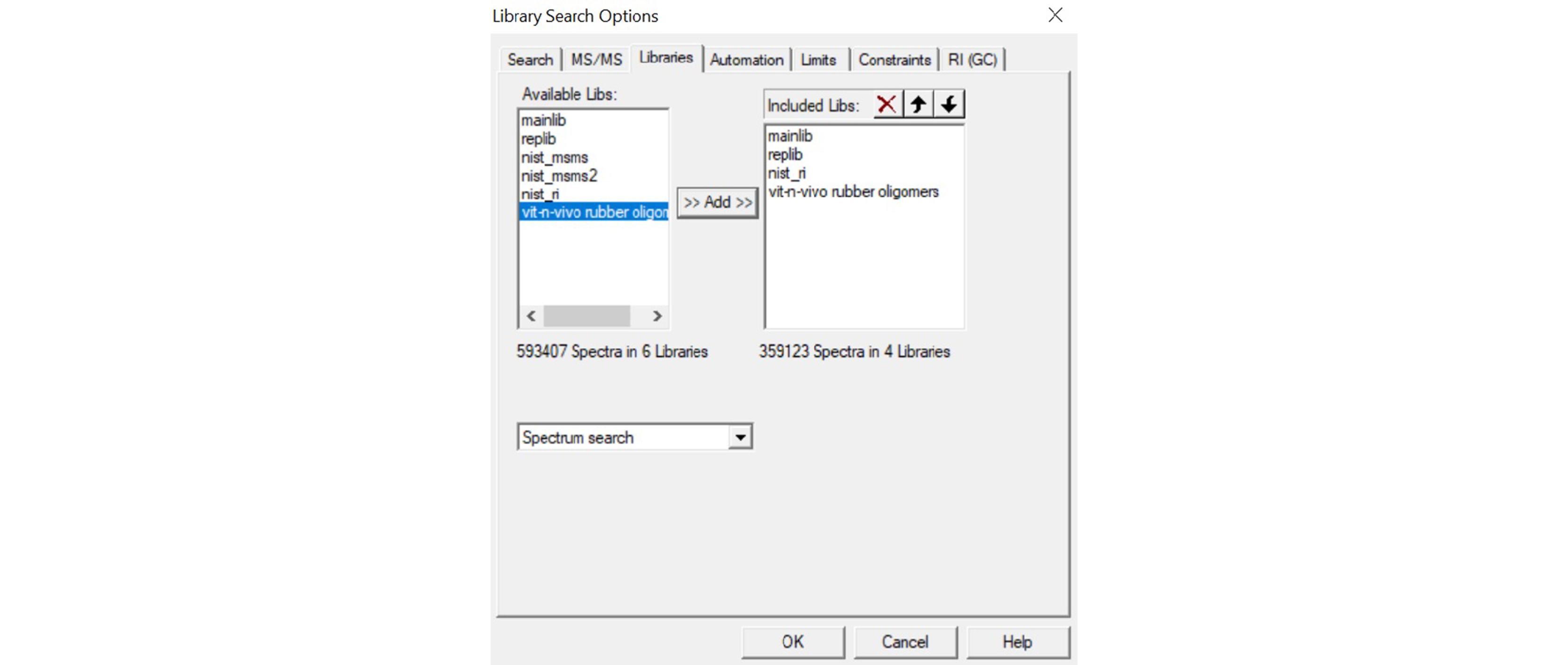
Figure 12. Library Search Options Libraries tab
Figure 12. Library Search Options Libraries tab
Third, perform NIST MS Search to check if your samples contain rubber oligomers.